TT-CSIRT – 449.22.08.25 – Microsoft 365 ADFS Exploit
Please be advised, a sophisticated phishing campaign have been uncovered, that exploits Microsoft’s Active Directory Federation Services (ADFS) to create legitimate-looking login URLs that redirect users to malicious credential-harvesting sites, effectively turning Microsoft’s own infrastructure into an unwitting accomplice in credential theft operations.
Exploit
Malicious Google ads clicked on by users who are then redirected through a complex chain that ultimately leads to authentic-looking Microsoft login pages designed to steal credentials and bypass multi-factor authentication (MFA) through adversary-in-the-middle (AiTM) techniques.
Method
Threat actors creates custom Microsoft tenants with ADFS configured, generating legitimate office.com URLs that Microsoft’s servers will redirect to attacker-controlled domains, abusing Microsoft’s ADFS infrastructure.
Dubbed “ADFSjacking”, the technique mirrors the SAMLjacking attack technique but exploits Microsoft’s federation services instead. This is essentially an open redirect vulnerability, attackers found a way to redirect from a legitimate outlook.office.com link to a phishing Website.
The fake domains are leveraged, like bluegraintours[.]com, which appears to be an AI-generated travel blog designed to evade domain categorization systems used by security tools.
The phishing sites themselves employ reverse-proxy configurations to intercept user sessions during authentication, effectively stealing both credentials and session tokens to bypass MFA protections.
This conditional loading technique prevents automated analysis tools from fully recreating the attack flow, adding another layer of evasion.
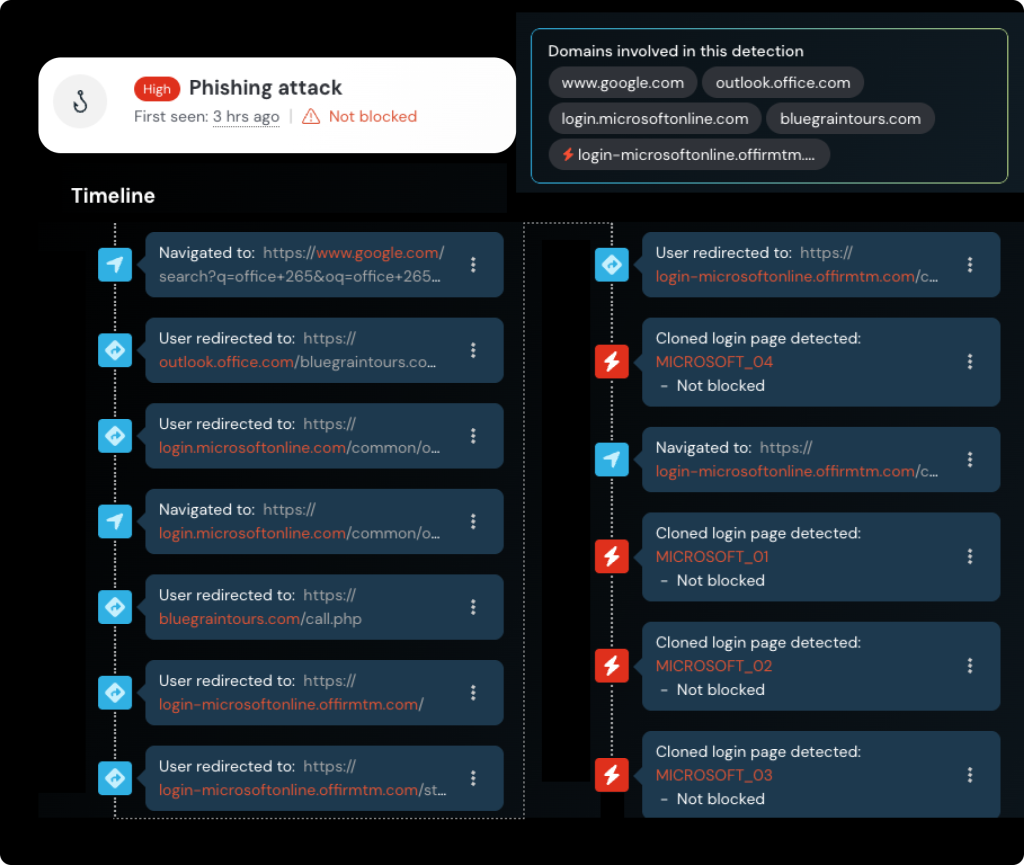
Illustration of exploit execution
Recommendations
- Monitor proxy logs for suspicious ADFS redirects, particularly those directing to unauthorized domains with /adfs/ls/ in the path, to identify potential threats.
- Monitor for Google redirects to office.com containing advertisement parameters, which may indicate malvertising-based attacks.
- Deploy enterprise-wide ad blockers to reduce exposure to malvertising campaigns, though attackers continue to diversify their delivery methods beyond traditional advertising channels.
- Implement behavior-based detection system to identify malicious activity regardless of the delivery mechanism or infrastructure abuse employed by threat actors.
References
